Rocket Propulsion
What is a rocket?
A rocket can be various things but most commonly a rocket is
a tall, thin, round vehicle that propels into space. A particular engine can
also be called a rocket and any vehicle with that engine can also be labelled a
rocket.
How Does a Rocket
Engine Work?
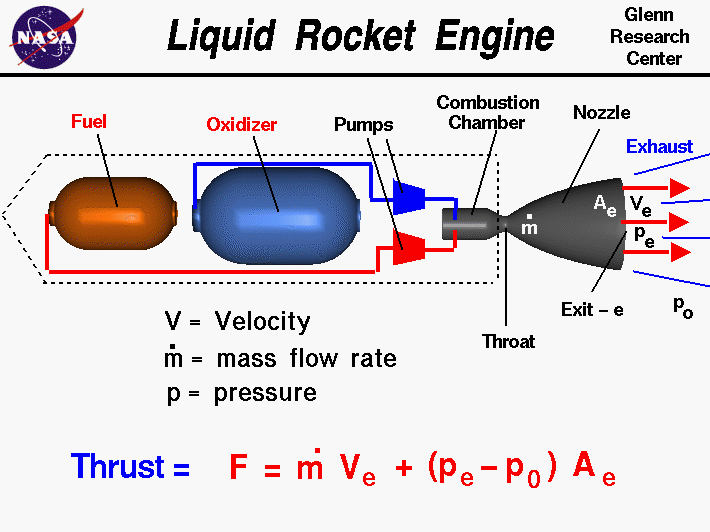
 Along with most engines, rockets burn fuel. Most rocket
engines turn the fuel into hot gas. The engine shoves the gas out its back. The
gas makes the rocket propel forward. There are two main types of rocket
engines. Some rockets use liquid fuel whereas others use solid fuels. The main
engines on the space shuttle orbiter use liquid fuel. On the side of space
shuttles are two white, solid rocket boosters that use solid fuels.
Along with most engines, rockets burn fuel. Most rocket
engines turn the fuel into hot gas. The engine shoves the gas out its back. The
gas makes the rocket propel forward. There are two main types of rocket
engines. Some rockets use liquid fuel whereas others use solid fuels. The main
engines on the space shuttle orbiter use liquid fuel. On the side of space
shuttles are two white, solid rocket boosters that use solid fuels.
In space, an engine has nothing to push against. Rockets
work by a scientific rule called Newton's third law of motion. More than 300
years ago, scientist, Sir Isaac Newton listed three Laws of Motion. The third
law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The
rocket pushes on its exhaust thus the exhaust pushes the rocket, too. The
rocket pushes the exhaust backward. The exhaust makes the rocket travel
forward.
When Were Rockets
Invented?
The first rockets ever knowingly created were in China in
the 1200s. These solid rockets were used for fireworks. Also various armies
used them in wars. In the next 700 years, people made bigger and better solid
rockets. Many of these were used for wars too. Using a Saturn V rocket in 1969, USA launched the first men to land on the moon.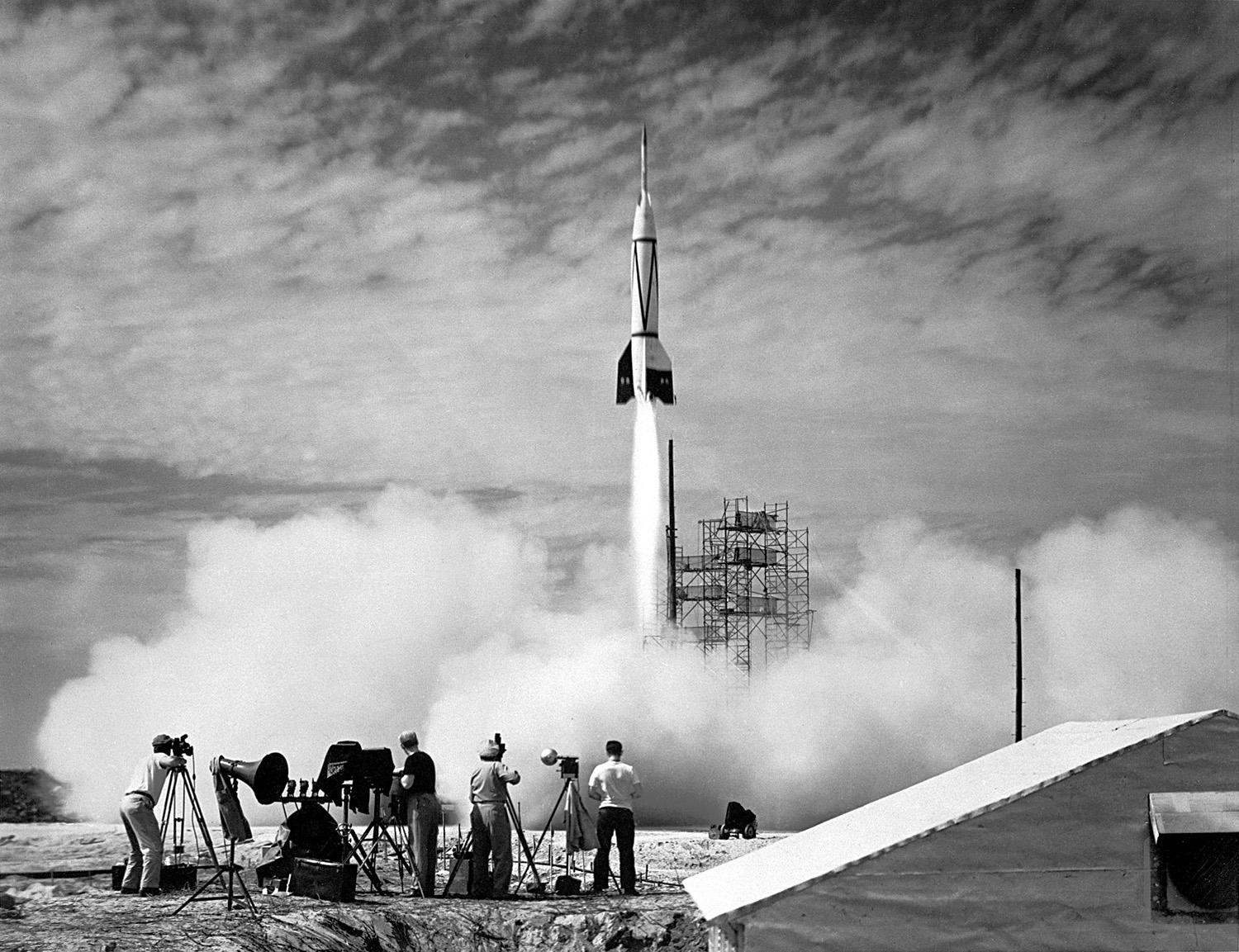 

first rocket ever launched (Cape Canaveral July 1950)


No comments:
Post a Comment